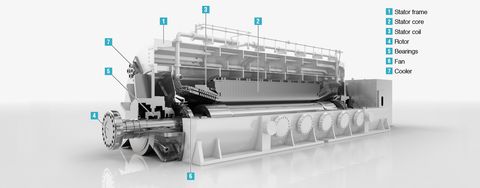
Beginner’s Guide to Electrical Connectors: Basics and Introduction
Electrical connectors are devices designed to join electrical circuits together, allowing current or signals to flow reliably between components. They exist in nearly every modern system, from household appliances and smartphones to industrial machinery and automobiles.
The development of connectors began with the need to simplify assembly, maintenance, and repair of electrical systems. Instead of permanently soldering wires, connectors provide a detachable and reusable solution. Over time, innovations in safety, material science, and miniaturization have expanded their use across industries.

Importance
Electrical connectors matter because they make complex systems safe, efficient, and scalable:
-
Safety – Connectors prevent loose wiring, reduce risks of short circuits, and provide insulation against electrical shock.
-
Convenience – They allow quick assembly and disassembly, saving time in maintenance or upgrades.
-
Standardization – Common connector types ensure compatibility between devices and components.
-
Versatility – From USB ports in laptops to heavy-duty connectors in aircraft, they serve diverse purposes.
-
Global Impact – They affect consumers, electricians, engineers, manufacturers, and industries ranging from electronics to renewable energy.
Without connectors, building and maintaining modern systems would be slower, more dangerous, and more expensive.
Recent Updates
The connector industry continues to evolve, influenced by technology trends and market demand:
-
Miniaturization (2023–2024) – Connectors are becoming smaller to fit compact devices such as wearables and IoT sensors.
-
High-Speed Data Connectors – The demand for USB-C, Thunderbolt, and fiber-optic connectors increased in 2023 due to faster data transfer requirements.
-
Sustainability Efforts – Manufacturers are exploring recyclable materials and eco-friendly production processes.
-
Electric Vehicle Growth (2024) – EV charging connectors are gaining global attention, with new standards like CCS and NACS competing in different regions.
-
Smart Manufacturing Integration – Industrial connectors now support automation systems, providing both power and data connectivity for advanced robotics.
A quick overview of trends can be seen below:
| Trend | Impact Area | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Miniaturization | Consumer electronics | Wearables, IoT devices |
| High-speed data transfer | Computing & communications | USB-C, Thunderbolt |
| Sustainability focus | Manufacturing materials | Recyclable plastics |
| EV charging standards | Automotive industry | CCS, NACS |
| Industry 4.0 integration | Automation & robotics | Smart connectors |
Laws or Policies
Electrical connectors are regulated to ensure safety, interoperability, and environmental compliance. These regulations vary by country but often include:
-
Safety Standards – Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) set safety requirements.
-
RoHS Directive (EU) – Restricts hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium in connectors.
-
WEEE Directive (EU) – Governs recycling and disposal of electronic components, including connectors.
-
FCC & CE Marking (US & EU) – Certify that electronic devices and connectors meet electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements.
-
Automotive Standards – Specific to EV charging, governments are setting connector standards (e.g., the U.S. adoption of NACS in 2023).
These policies protect both consumers and the environment while ensuring international trade compatibility.
Tools and Resources
Beginners can explore several tools and resources to better understand or work with connectors:
| Tool/Resource | Use |
|---|---|
| Molex & TE Connectivity Catalogs | Databases of connector types and specifications |
| Digi-Key & Mouser | Online suppliers with datasheets and compatibility guides |
| Connector Selector Tools | Available on many manufacturer websites to choose correct connectors |
| Electrical Engineering Apps | Mobile apps (e.g., ElectroDroid) for pinouts, wire sizes, and circuit helpers |
| YouTube Tutorials | Step-by-step demonstrations of connector assembly and testing |
| IEEE Standards Library | Reference materials for professional and academic users |
These resources allow both hobbyists and professionals to identify, source, and apply the right connectors in different projects.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main types of electrical connectors?
A: Common categories include power connectors, data connectors, audio/video connectors, and automotive/industrial connectors. Examples are USB, HDMI, coaxial, and circular connectors.
Q2: How do I choose the right connector?
A: Consider current capacity, voltage rating, environmental conditions (humidity, dust, vibration), and compatibility with your device or system.
Q3: What is the difference between male and female connectors?
A: Male connectors have pins that insert into female connectors, which contain sockets. This design ensures secure and correct connections.
Q4: Can connectors wear out over time?
A: Yes. Mechanical stress, corrosion, or repeated plugging/unplugging can degrade connectors. High-quality connectors are designed for durability, but regular inspection is important.
Q5: Are all USB connectors the same?
A: No. There are multiple versions (USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, micro-USB), each with different shapes, power capabilities, and data transfer speeds.
Conclusion
Electrical connectors may appear small, but they are the backbone of modern technology. From ensuring safe household wiring to enabling global communication systems, connectors play a crucial role in everyday life.
The industry continues to advance, with recent trends in miniaturization, EV charging solutions, and eco-friendly production shaping the future. Regulatory standards add a layer of safety and accountability, while digital tools and guides help beginners understand and work with connectors more effectively.
For anyone starting out, learning the basics of connectors provides valuable knowledge not only for personal projects but also for understanding the systems we rely on daily.