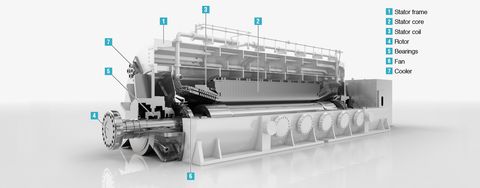
From drawing and stranding to insulation and sheathing, each step in cable production requires specific machinery working in sync. The purpose of cable manufacturing machines is to automate and streamline these processes, ensuring uniformity in cable quality, improving productivity, and reducing material waste.
With global demand for high-performance cables growing due to smart infrastructure, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy systems, understanding how these machines work has become more important than ever.
Why Cable Manufacturing Machines Are Important Today
Who Benefits from Cable Manufacturing Machines?
-
Manufacturers – Cable producers rely on advanced machinery to increase throughput, reduce downtime, and comply with international quality standards.
-
Engineers and Technicians – Understanding how these machines work helps with maintenance, troubleshooting, and optimization.
-
Students and Researchers – Offers insights into modern industrial automation and mechanical engineering.
-
Policymakers and Regulators – Helps ensure compliance with safety and quality regulations in infrastructure projects.
Problems Solved by Cable Manufacturing Machines:
-
Manual Labor Limitations – Replaces tedious, time-consuming tasks with automated precision.
-
Inconsistent Product Quality – Reduces human error and ensures uniform cable characteristics.
-
High Material Waste – Optimizes the use of copper, aluminum, insulation, and sheathing materials.
-
Production Bottlenecks – Increases speed without compromising quality, supporting larger-scale manufacturing.
Applications Across Industries:
| Industry | Use of Cables |
|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Fiber optics for high-speed internet and data |
| Automotive | Wiring harnesses for EVs and smart vehicles |
| Construction | Power cables and building automation wiring |
| Renewable Energy | Solar and wind energy transmission cables |
| Aerospace | Lightweight shielded cables for avionics systems |
Trends and Updates in Cable Manufacturing
Over the past year, several advancements and shifts have taken place in the cable manufacturing sector:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration – Smart monitoring systems now help predict machine failures and optimize production lines in real-time.
-
Eco-Friendly Cable Production – Manufacturers are adopting biodegradable sheathing materials and lead-free insulation in response to environmental regulations.
-
Digital Twin Technology – Virtual modeling of cable manufacturing lines allows testing and improvements without physical changes.
-
Rise in EV Demand – Increased production of cables with high voltage and thermal resistance, especially in Asia and Europe.
-
Automation Expansion in Developing Markets – Countries like India, Vietnam, and Brazil have increased investments in semi-automated and fully automated cable machinery.
According to a 2025 report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cable and wire manufacturing equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2029, driven largely by infrastructure modernization and renewable energy needs.
Government Policies and Regulations Impacting Cable Manufacturing
Cable manufacturing is subject to strict standards and regulations, often varying by country or region. Below are some key frameworks:
-
IEC Standards (International) – International Electrotechnical Commission standards govern the quality and safety of cables and equipment globally.
-
RoHS (EU Directive) – Restriction of Hazardous Substances directive requires the elimination of materials like lead and mercury in electrical components.
-
BIS Certification (India) – The Bureau of Indian Standards mandates safety and quality for electric cables used in domestic and industrial wiring.
-
NEC (United States) – The National Electrical Code dictates design and performance criteria for cables in the construction industry.
-
REACH Regulation (Europe) – Ensures that chemical components in cable insulation and jackets do not pose health or environmental hazards.
Some regions also offer incentives and subsidies for adopting energy-efficient machinery and automation tools in manufacturing setups, as part of green technology programs.
Helpful Tools and Resources for Learning and Implementation
Whether you're a technician, student, or manufacturer, there are a variety of resources to support your understanding of cable manufacturing machinery:
Educational Platforms:
-
Coursera – Offers basic and advanced industrial automation courses, including modules on cable manufacturing.
-
MIT OpenCourseWare – Free engineering courses, including materials science and mechanical systems relevant to cable production.
-
edX – Hosts automation and mechanical design programs from global universities.
Technical Documentation and Standards:
-
IEC Webstore – Purchase or view international cable machinery and safety standards.
-
IEEE Xplore Digital Library – Access to technical papers on cable machinery innovation and engineering.
Software Tools:
| Tool Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| AutoCAD Electrical | Design and simulate cable schematics |
| EPLAN Electric P8 | Advanced planning and documentation of wiring |
| COMSOL Multiphysics | Simulate thermal and electrical properties of wires |
-
Wire & Cable India – News and updates on Indian cable manufacturing.
-
Wire World – Global directory of cable machinery suppliers and industry events.
-
Interwire Conference (USA) – Annual event focused on wire and cable production innovations.
Support Services:
-
Local Trade Associations – Many regions have cable manufacturing councils offering training and compliance guidance.
-
Machine Suppliers – Major companies like NIEHOFF, Maschinenfabrik Niehoff, and SAMP provide setup manuals and training materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What types of machines are used in cable manufacturing?
Cable manufacturing lines generally include wire drawing machines, stranding machines, extrusion machines, armoring machines, and coiling units. Each machine performs a specific task in the cable-making process.
2. How do wire drawing machines work?
These machines reduce the diameter of a metal rod (usually copper or aluminum) by pulling it through a series of progressively smaller dies. Lubricants and cooling systems are used to maintain smooth operation and prevent wire damage.
3. Can one machine make all types of cables?
No, different cables require different production setups. For example, fiber optic cables use completely different equipment compared to power cables. Some high-end lines may be modular to support varied production types.
4. Are cable manufacturing machines expensive to maintain?
Maintenance costs vary depending on machine type, usage frequency, and manufacturer support. However, modern machines often come with predictive maintenance tools that help minimize unexpected downtime and long-term costs.
5. Is it possible to start a small-scale cable manufacturing unit?
Yes, it is possible, especially for low- to medium-voltage cables. There are semi-automatic systems designed for small setups. However, regulatory compliance, space requirements, and quality assurance are still essential considerations.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how cable manufacturing machines work not only benefits those directly involved in production but also supports broader developments in engineering, automation, and industrial efficiency. As demand grows for smarter, safer, and more sustainable wiring solutions, knowledge of cable manufacturing technology becomes increasingly valuable. With a variety of learning tools and global innovations at hand, even beginners can start to grasp this complex but essential industrial process.